Sudamina Or Miliaria: What Is It?
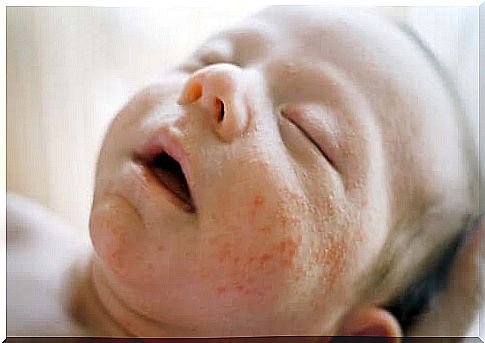
Sudamine, also called miliaria, is a rash. It often affects newborns, but can occur at any age.
This type of rash occurs as a result of obstruction of the ducts of the sweat glands, which are responsible for carrying sweat to the most superficial layer of the skin. As a result of the obstruction, itching, inflammation and small blisters are produced.
All very annoying symptoms. It usually occurs in the summer, especially in very hot and humid climates. It usually goes away on its own.
Because of how often it occurs and because it can become very annoying for sufferers (and cause for concern for parents), we explain everything you need to know about sudamine.
What does sudamine consist of?
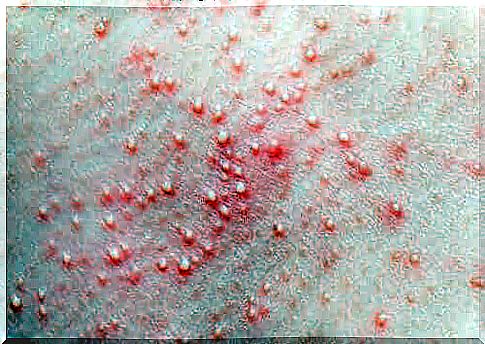
Sudamine (or miliaria) is a rash that occurs due to obstruction of the excretory ducts of the sweat glands. These channels allow sweat to reach the most superficial layer of the skin, promoting perspiration.
In case of obstruction, instead of evaporating, the sweat is trapped under the skin surface causing inflammatory reactions that manifest themselves with rashes, itching and other symptoms.
The causes of this obstruction are not fully known. It is believed that one of the reasons could be an incomplete development of the excretory ducts that tend to become obstructed. This would explain why it is mostly babies who suffer from sudamine.
Another factor that favors its appearance is living in hot and humid environments. Any activity that makes you sweat, in fact, seems to be decisive for the onset of this problem.
On the other hand, it has also been observed that sudamine often affects people who are sick and who have remained at rest for some time. In particular, it mainly affects those who have had a fever.
What are the symptoms of sudamine?
It is important to know that the rash usually appears on the places where the skin is most prone to friction. For example, in newborns it occurs between the folds of the buttocks, on the neck or below the chest. Very often it even affects the armpits and groin.
Furthermore, it is accompanied by itching and irritation and affects the different skin layers in more or less aggressive forms (which is why it can vary depending on the subject).
In milder cases it affects only the most superficial layer of the skin. Therefore, in addition to the rash, blisters appear that are easily eliminated but which, however, can cause pain.
When it affects the deeper layers of the skin, red, more painful bumps appear. Curious fact: these cases manifest themselves with a tickling sensation in the affected area. Sometimes these bumps fill with pus and become inflamed, causing the infection to get worse.
Sudamine can lead to a more severe form, although it rarely happens. In these cases, it affects the deeper skin layers and causes noticeable, red lesions on the skin.
What is the proper treatment?
Sudamine does not require treatment in most cases. However, some measures help relieve symptoms. For example, it is important to live in a cool and well-ventilated environment.
Also, it would be wise to avoid clothing that is too tight or wearing too many layers of clothing. If it is summer, try to wear light and cool clothing. In the case of newborns, the same applies, but also make sure to protect them from the heat.
If you have a severe form of sudamine, you may need to apply ointments or lotions to get relief from symptoms. In some cases, it may be necessary to prescribe topical corticosteroids to calm the inflammation.

To conclude
Sudamine (also known as miliaria) is a rash that usually affects infants living in warm, humid environments. It generally does not present complications or in severe clinical pictures.
However, it is essential to contact the doctor in front of any type of symptom, in order to rule out that it is another pathology.