Allergy To Food Additives: Symptoms And Treatment

Allergy to food additives is a problem that often goes unnoticed, because it is confused with intolerance to a food. In reality, these are two different phenomena, which nevertheless have a common origin and present similar symptoms.
In the case of food intolerance, the digestive system becomes irritated because the person has difficulty in adequately assimilating a food or a food additive. In the case of allergy to food additives and to foods in general, however, the immune system reacts disproportionately, to the point of putting the person’s life at risk.
In general, people pay much more attention to food intolerances or allergies than to allergy to food additives. The reason is that, even though these latter substances are present in most processed foods, those who consume them are unaware of their potential danger.
Food additives
Food additives are substances that are added to processed foods during their preparation. They allow you to modify the food in terms of flavor, texture, color, aroma or storage time. These substances are added with the clearance of the health authorities and must appear on the product label.
Allergy to food additives occurs when the body detects one of these substances as potentially dangerous. Consequently, an immunological reaction is triggered destined to attack the additive, presenting symptoms that can become very serious.
Symptoms of allergy to food additives
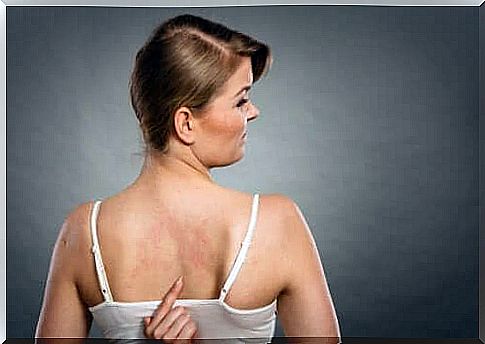
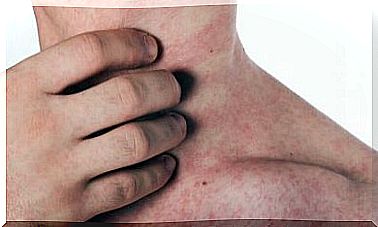
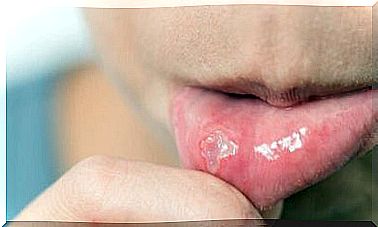
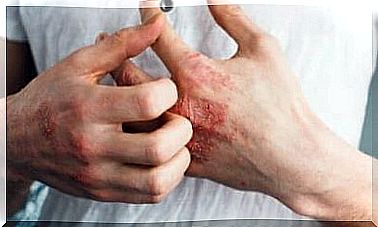
Symptoms of food additive allergy can vary greatly. However, the most frequent are those of a respiratory nature, in particular asthma and rhinitis; and those of a cutaneous nature, mainly urticaria, and the different forms of dermatitis.
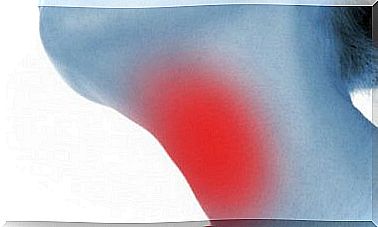
Symptoms can evolve to trigger a severe reaction called anaphylaxis, which is life-threatening. It occurs quickly and violently and is due to the massive release of histamine and other substances. It leads to constriction of the airways and eventually death.
Currently, 5% to 10% of chronic urticaria cases are thought to be due to allergy to food additives. However, the figure could be even higher. Nowadays, intolerance to certain foods can be an alarm signal that should be brought to the attention of the allergist.
Potential risk of some additives
Each food additive is capable of causing different reactions. However, some have a higher risk potential. Are the following:
- Antioxidants. There have been reports of urticaria and atopic dermatitis caused by the ingestion of foods containing industrial antioxidants. In a few cases, episodes of bronchospasm result.
- Sulfur dioxide and sulphites. Sulphites can cause respiratory symptoms, such as rhinitis and acute relapses in asthmatics. They could also cause contact dermatitis, hives, or digestive problems.
- Nitrates and nitrites. They are associated with the aggravation of atopic dermatitis and with cases of severe allergic reactions.
- Benzoic acid and benzoates. They are the additives most associated with allergic reactions. They cause acute relapses of atopic dermatitis and asthma, hives, headaches, migraines, difficulty concentrating and hyperactivity.
- Methylcellulose. It is associated with harmful gastrointestinal reactions.
- Gelatin E441. It is a thickener that can cause severe allergic reactions.
- Guar gum and tragacanth gum. The former can cause gastrointestinal problems. The second can aggravate atopic dermatitis or cause hives.
- Monosodium glutamate. It can cause severe allergic reactions.
- Dyes. They are capable of causing mild, moderate or, on rare occasions, severe allergic reactions.
Treatments

There is no effective treatment for allergy to food additives. The only choice available is to eliminate them from the diet. However, this could be a difficult task, as there are so many foods these days that contain additives with allergic potential.
Furthermore, sometimes additives are not identified by their name, but by a reference number. It is important to do research on the name of components that match a certain number or code. The best countermeasure, therefore, is to avoid precooked or prepared foods of industrial origin.
The lower the extent to which a food has been industrially processed, the lower the amount of additives it contains. The best diet is one made up of fresh foods of natural origin. In addition, it is important to avoid eating foods whose nutritional information is not clearly stated. In these cases, the best choice is to refrain from eating them.