Cold Urticaria: Risk Factors And Prevention

Cold urticaria is a skin reaction that occurs shortly after exposure to cold. Red, itchy bumps appear on the skin.
This condition is more common in young adults and is one of the 5 most common causes of chronic urticaria, including in the physical type.
As mentioned, this skin condition appears after exposure to the cold. However, it can also occur after contact with an object, air or cold liquid.
Cold urticaria is also known as a cold allergy, as its skin manifestations occur 10-30 minutes after exposure. On other occasions, it can appear at the same time.
Cold urticaria symptoms
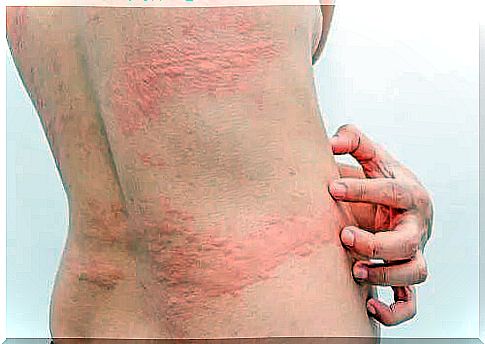
People with cold urticaria experience very different symptoms. Some of the most common are:
- Urticaria : As the name suggests, it is the main symptom. Itchy rashes appear temporarily on areas that have been exposed to the cold.
- When the skin heats up, the reaction worsens.
- Swelling of the hands when holding cold objects.
- Swelling of the lips when consuming cold foods and drinks.
In other cases, the symptoms are not as mild. Fever, malaise, and localized pain in the head, abdomen, or joints may occur. In addition, some people experience very severe symptoms affecting the oropharyngeal tract, namely the mouth, glottis and trachea.
In case of prolonged exposure to cold, such as a cold water bath in a natural environment, the patient can suffer from anaphylaxis and drown. This occurs because the passage of air is interrupted due to an oropharyngeal angioedema.
Causes and risk factors
Currently, the exact causes of cold urticaria are unknown. In some cases it appears to be due to extreme cellular sensitization due to an inherited trait, virus or disease.
Normally, when a person suffers from this condition, the cold triggers the release of histamine and other substances. Their joint action causes the symptoms mentioned in the previous paragraph.
On the other hand, a number of risk factors favor the appearance of cold urticaria. Among these we can mention:
- Age : Young adults are the most likely to suffer from it.
- Undiagnosed condition : There is a type of secondary acquired cold urticaria that may be due to an undiagnosed health problem, such as hepatitis.
- Inheritance : Cold urticaria is sometimes inherited.
How to prevent this ailment?
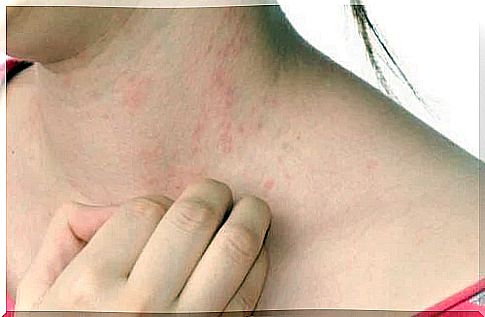
Some measures can be taken to prevent recurring episodes of cold urticaria. Among these, we recommend the following:
- Consult your doctor about the most suitable antihistamine for your specific case. Follow the prescribed treatment.
- In case you need to expose yourself to the cold, protect yourself with suitable clothing.
- If you go swimming, try dipping your hand in the water first to see if a skin reaction occurs.
- If your doctor has prescribed an epinephrine auto-injector for you, always take it with you to avoid severe reactions.
- Tell your doctor about your cold urticaria if you are undergoing surgery.
Treatment of cold urticaria
Cold urticaria is mainly treated with antihistamine drugs. These are drugs that calm the symptoms but do not prevent them.
However, the use of antihistamines is not effective for all types of cold urticaria. Today there are other more specialized pharmacological treatments, which are applied at the discretion of the dermatologist.
Another option is to increase the patient’s tolerance to cold. In this case, you gradually increase your exposure to cold temperatures. However, this should always be done in the hospital and under medical supervision.
Despite this, the ideal is always to prevent, this means avoiding exposure to the cold as much as possible.