Osteoarthritis Of The Hip: What It Is And What Are The Symptoms
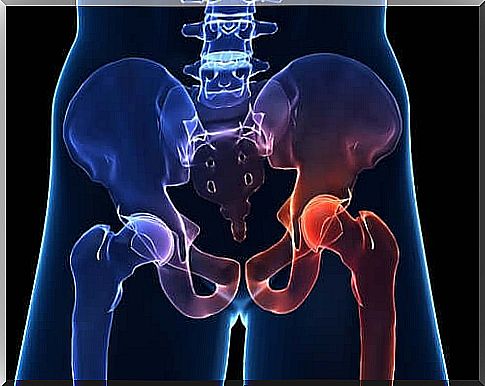
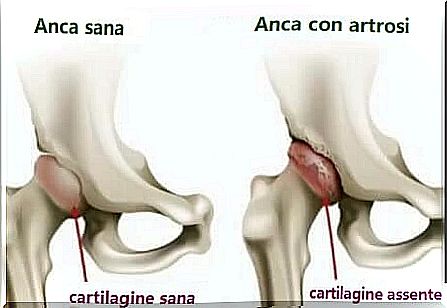
Osteoarthritis of the hip is the wear and tear of hyaline cartilage. This covers the joint to protect it from slipping and mitigate any overloads.
An imbalance due to trauma, a genetic defect, and even misuse of the joint can reduce the cartilage’s ability to hold water. This phenomenon causes progressive wear of the joint which causes deformation of the bones. Following this, pain and loss of mobility are felt.
Causes and risk factors
The cause of hip osteoarthritis is unknown, although several factors favor its occurrence, such as genetic inheritance. It is therefore possible to inherit osteoarthritis.
Even limb malformations can predispose to its appearance, particularly in the lower extremities, which are intended to support the weight of the body. Being overweight or obese contributes to overloading the hips and knees, increasing the possibility of wear and tear.
Even intense sports practice can favor the onset of osteoarthritis, especially in the lower extremities, as well as certain professions. Finally, repeated trauma can cause premature osteoarthritis, since a fracture can prevent the joint from re-fitting properly.
Symptoms of hip arthrosis
The main symptom is pain in the groin, thigh, inner thigh and even in the knees. Pain is usually associated with activity and subsides with rest; it is called “mechanical” and differs from inflammatory joint pain. The latter, in fact, persists even in a state of rest. Generally it affects only one hip or especially one, but it is not excluded that it can affect both.
Another symptom of hip osteoarthritis is loss of movement, a condition that makes it difficult to perform various daily actions. Both the pain and the disability are progressive, even if the course differs according to the case.
Limping is another symptom associated with hip osteoarthritis. If it affects both joints, it is accompanied by a characteristic rocking of the body.
Osteoarthritis of the hip has a slow course, sometimes for years, depending on the activity that is at the origin. Thanks to proper treatment, many people are able to lead normal lives.
Osteoarthritis of the hip: diagnosis
The diagnosis is made after the patient has answered a few questions about the symptoms and their characteristics. An exploration of the joint and its movements is also carried out. In this way the specialist is able to assess the degree of osteoarthritis present.
An x-ray is taken to confirm the diagnosis in light of the changes found in the joint. It is thus possible to formulate a prognosis as a function of the extent of wear.
There is no direct relationship between the intensity of wear and the symptoms. However, a heavily worn hip may not cause any pain, but it will be stiffer, and vice versa.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip
Treatment of osteoarthritis is aimed at calming pain and recovering functional capacity. For this purpose, the doctor will prescribe some medications to the patient.
- Analgesics : these are the most prescribed medicines. They calm pain and improve joint stiffness. The most common analgesic is paracetamol.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, used especially when the pain is more acute.
- Chondroprotectors : substances that make up the articular cartilage and that calm pain. This group includes glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate.
- Intra-articular therapy or infiltrations : some anti-inflammatory substances are administered directly into the joint. In most cases these are glucocorticoids and, more recently, hyaluronic acid.
In addition, the doctor will advise you to maintain a healthy lifestyle and, if necessary, will suggest some measures to calm the discomfort, such as applying cold packs and resorting to physiotherapy.
According to Dr. Alexandra Villa-Forte, “ the application of cold (for example by means of ice packs) calms the pain caused by joint infiltration”.
Healthy habits: the best remedy for hip osteoarthritis
Adopting and maintaining good postural hygiene, avoiding excessive or incorrect use of the joints, exercising regularly, taking measures to prevent or treat obesity and using appropriate footwear are some of the precautions most recommended by experts for the well-being of affected patients. from osteoarthritis of the hip.
It is important to emphasize that the practice of physical exercise must respond to the physical condition of the subject. Therefore, he should always consult his doctor.